Sometimes, flaws are what makes a thing special. That’s the case for a type of material called optical quantum emitters, which send out light in an exceptionally precise manner, one photon at a time, often due to tiny imperfections in a crystal’s structure. The ability to emit light one photon at a time could allow optical quantum emitters to become the backbones of ultrafast computers, super high-resolution sensors and uncrackable long-range secure communication technologies.
A promising alternative to conventional power plants, solid oxide fuel cells use electrochemical methods that can generate power more efficiently than existing combustion-based generators. But current fuel cell technologies tend to degrade too quickly, eating up any efficiency gains through increased cost. Now, in an advance that could help lead the way toward longer-lived green energy devices, engineers at the University of Wisconsin-Madison have revealed new insight about the chemical reactions that power fuel cells.
Media coverage of WEI this month focused on UW–Madison students learning by doing, the Midwest as an energy innovation hub, and how GLBRC research is honing in on more valuable products for the biofuels industry.
A survey of the world’s top universities placed the University of Wisconsin–Madison as the seventh-greatest source of U.S. patents.
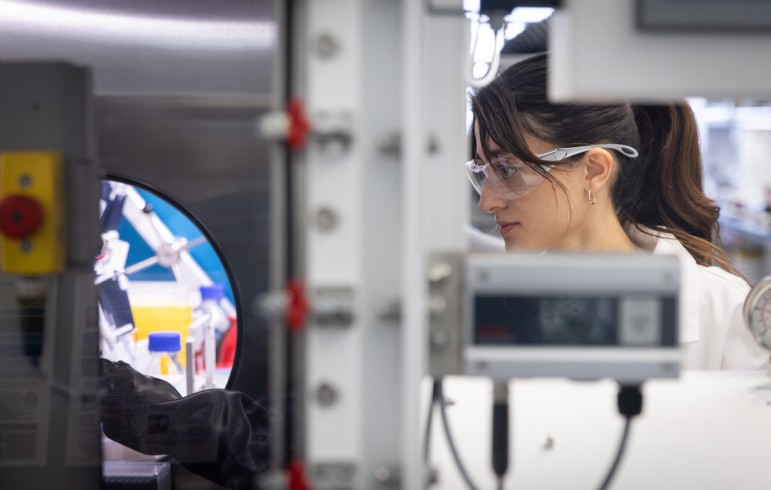
The University of Wisconsin–Madison and the American Chemical Society are partnering to train more underrepresented minority students in chemical research to increase the numbers of these students in chemistry doctoral programs.
Last year, the Wisconsin Energy Institute asked five students about their motivations for studying energy.
Diesel and jet fuels are notoriously difficult to obtain from non-oil plant-based sources, which is a major hurdle in biofuels research.