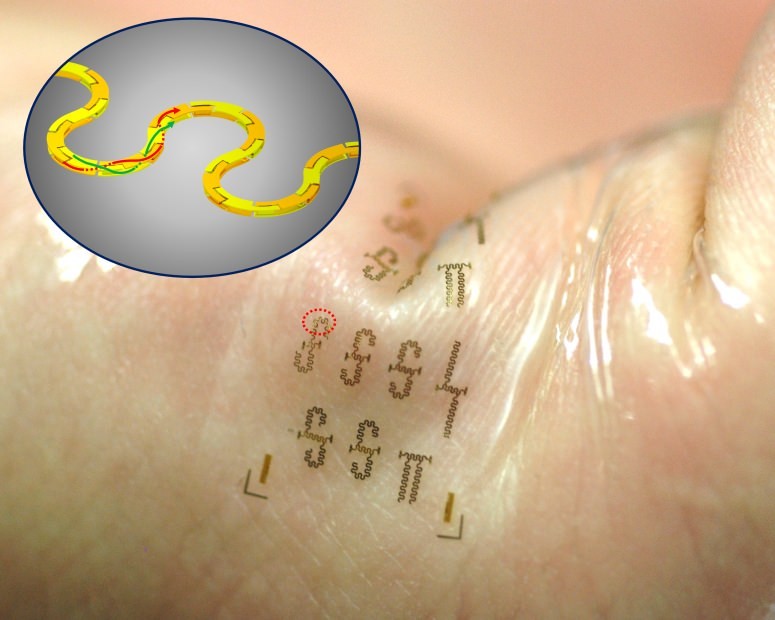
The consumer marketplace is flooded with a lively assortment of smart wearable electronics that do everything from monitor vital signs, fitness or sun exposure to play music, charge other electronics or even purify the air around you — all wirelessly.
Now, a team of University of Wisconsin—Madison engineers has created the world’s fastest stretchable, wearable integrated circuits, an advance that could drive the Internet of Things and a much more connected, high-speed wireless world.
Led by Zhenqiang “Jack” Ma, the Lynn H. Matthias Professor in Engineering and Vilas Distinguished Achievement Professor in electrical and computer engineering at UW–Madison, the researchers published details of these powerful, highly efficient integrated circuits today, May 27, 2016, in the journal Advanced Functional Materials.





